tibial torsion test of ankle joint by physiotutors|femoral anteversion and tibial torsion : exporting Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of . Confira o placar da Loteria Nacional das 12 horas de hoje, o resultado da Loteria Nacional você confere aqui no site O Resultado. Pegue sua aposta e confira os .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBVideos tagged « novinhas ». (1,186 results) . VÍDEO AMADOR PRIMEIRA VEZ NOVINHO COMENDO AS DUAS NOVINHAS NO PELO SEXO A TRÊS. TRISAL. As .
Posterior tibialis tendon dysfunction, abbreviated as PTTD, is the major cause of an adult acquired flatfoot deformity and medial ankle pain. It is caused by chronic overuse and subsequent tendon inflammation which may impede . Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knees flexed to 90° over the edge of the examining table. the examiner places the thumb of one hand over the apex of one . In their work, tibial torsion was determined by the two most dorsal proximal points of the tibia and the two outermost points at the height of the ankle joint, a technique adapted .
The most accurate technique for measuring tibial torsion is anthropometric measurement on necropsy specimens. Although this approach is useful for establishing . Our results showed that clinical measurements of tibial torsion differences are highly accurate and have a great inter- and intra-observer reliability. Intraoperative tools for .
External Tibial Torsion is a rare developmental condition in young children caused by abnormal external rotation of the tibia leading to an out-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle measuring greater .The ankle consists of three joints; talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the Inferior tibiofibular joint. The talocrural joint is commonly known as the ankle proper and is a synovial hinge joint.To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with knees flexed to 90 o. A thigh-foot ankle (TFA) is measured between the line bisecting the posterior thigh and another line bisecting the foot.First and foremost let’s talk a little bit about anatomy. The ankle joint consists of two different joints: The talocrural joint, which is a hinge joint allowing the two primary movements in the sagittal plane: plantar flexion and dorsiflexion; The .
Tibial Torsion - TeachMe Orthopedics Tibial Torsion - TeachMe Orthopedics. Publisher - Learn Orthopedics with Ease . with the ankle and foot, is rotated internally or externally (i.e., inward or outward) on its .
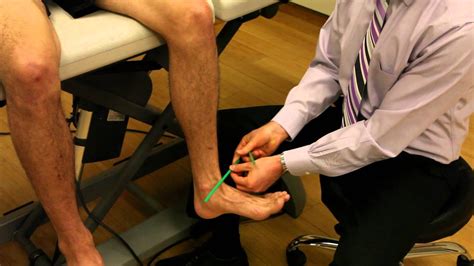
tibial torsion special test
The tibia is practically fixed between the knee and ankle joint, which have only minimal degrees of rotational freedom. In theory, this means that the foot can probably be reliably used as an indicator of tibial torsion if the knee joint and patella are positioned in a reproducible way, same for both lower limbs.Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn outward (external tibial torsion). Tibial torsion affects boys and girls in nearly equal numbers. The Talar tilt test assesses the stability of the ankle joint, specifically the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL) which connects the calcaneus (heel bone) to the fibula. We use it to help diagnose . The Squeeze Test for high ankle sprain is a diagnostic method that specifically assesses the integrity of the ligaments between the tibia and fibula .1. Sensitivity values for the Anterior Drawer test have been shown to be between 32% to 80% while specificity value has been reported as 80%. 2. A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific .
Journal of foot and ankle research. 2009 May 7;2(1):12.fckLRBibTeX; ↑ Stuberg W, Temme J, Kaplan P, Clarke A, Fuchs R. Measurement of tibial torsion and thigh-foot angle using goniometry and computed tomography. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 1991 Nov 1;272:208-12. ↑ Tibial Torsion Prone Test (CR). CRTechnologies.
GENERAL INFORMATION. Active movements of the lower leg, ankle, and foot should be done in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing positions (long leg sitting or supine lying), and the examiner should note any differences, because foot deformities and deviations, in addition to decreased range of motion (ROM), can lead to injury in other parts of the lower .
The Single-Leg Heel Raise test was the best test in terms of inter-rater reliability and best related to ultrasound changes in those with tibialis posterior tendinopathy . which can lead to severe joint deformity at its worst. . Jackson JB 3rd. Prevalence of Abnormal Ultrasound Findings in Asymptomatic Posterior Tibial Tendons. Foot Ankle .
tibial torsion in adults
physical therapy for tibial torsion
internal tibial torsion in adults
Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ.To conduct the test, the patient lies supine, the upper leg is supported by the table, the knee joint is flexed, and the ankle joint is held in 10-15° of plantarflexion. Then grasp the heel, while the patient’s foot lies on the anterior aspect of your forearm.
To conduct the test, have your patient in side-lying position so that the tibial nerve becomes accessible posterior to the medial malleolus. Then maximally dorsiflex the ankle, bring the foot into maximal eversion and bring the toes into maximal extension at the MCP joints hold this position for 5-10 seconds, while you palpate for tenderness on the tibial nerve.
Physiotutors Helping you become the best physiotherapist you can be . EP. 067: Step by Step – The Ultimate Guide to Ankle Sprains with Jente Wagemans . All podcasts. READ, LEARN, DISCUSS, APPLY. HIGHLIGHTED BLOG ARTICLES Education & Career. February 11, 2021 . What Can We Learn From the 30-second Chair Stand Test? See all.
Ankle joint (articulatio talocruralis) The ankle joint, also known as the talocrural joint, is a synovial joint that connects the bones of the leg, the fibula and tibia, with the talus of the foot. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations.. It is often described as a tenon and mortise joint, as the tibia and fibula act as a mortise and form a notch in which the body of . Supination resistance is a clinical outcome that estimates the amount of external force required to supinate the foot. A greater supination resistance may indicate greater loads on structures responsible for generating internal supination moments across the subtalar joint during static and dynamic tasks. As such, greater supination resistance may be an expected finding .to test the calcaneofibular ligament the examiner will adduct and invert the calcaneous into a varus position. the deltoid ligament is examined by abducting and everting the calcaneous into a valgus position. Talar TILT Special Test: POSITIVE TEST 2: A positive test will result in laxity and/or pain ; Sensitivity 67, Specificity 75, LR+ 2.7, LR .
Dejour et al. report that a tibial tuberosity trochlear groove distance (TT–TG) > 20 mm is generally considered pathological and as an indication for medial tibial tubercle transfer in symptomatic participants 15. Tibial rotation angle relative to the femur was defined as the relative rotational difference between the femur and the tibia 16.Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (TTS) is a rare compressive neuropathy of the tibial nerve or one of its branches as they pass under the flexor retinaculum. In the TTS literature, the tibial nerve is also referred to as the posterior tibial nerve and TTS is also known as .The results suggested that MRI is a reliable method for diagnosing injuries of the lateral ankle ligaments. The talar tilt test cannot evaluate the specific pathology of lateral ankle ligaments, but it was reliable in indicating complete double-ligament ruptures (anterior talofibular and calcaneo-fibular ligaments), when talar tilt was 15" or .
imbalance of ankle dorsiflexors and plantarflexors, resulting in plantar flexion of the hindfoot relative to the ankle, with normal mid- and forefoot alignment . associated with equinovalgus and external tibial torsion. Pathophysiology. caused by combination of adductor hallucis overactivity and externally applied forces, such as inadequate .
A common orthopedic test to assess for possible plantar fasciitis is the Windlass Test. References. Picciano, A. M., Rowlands, M. S., & Worrell, T. (1993). Reliability of open and closed kinetic chain subtalar joint neutral positions and navicular drop test. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 18(4), 553-558.A simple assessment you can use is a single-leg squat and observe for the movement quality (femoral torsion, tibial torsion, valgus/varus, compensatory movement of the foot) as these may result in increased internal rotation or adductor moments in case of weak hip abductor/external rotator muscles.
bespoke Impact Testing
The dial test is a common test to diagnose PLC injuries and to distinguish them from posterior cruciate ligament tears. According to Krause et al. (2013), the dial test has intratester reliability of 0.83 to 0.89 and inter-tester reliability between 0.74 and 0.83 in healthy persons if a handheld inclinometer is used. The validity of this test .
Evidence [edit | edit source]. The squeeze test has been found to have moderate reliability (kappa = 0.50) according to a study performed by Alonso et al. and according to the study done by de César PC et al, the test has a sensitivity of 30% and a specificity of 93.5% for a high ankle sprain. In the study done by Sman AD et al, it is recommended that though the squeeze test . Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, and about two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. [1, 2] Tibial torsion can persist into adulthood and give rise to patellofemoral pathology.Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is an umbrella term used for pain arising from the patellofemoral joint itself, or adjacent soft tissues. It is a chronic condition that tends to worsen with activities such as squatting, sitting, climbing stairs, and running. . lateral tibial torsion, genu valgum or varus, increased Q-angle, tightness in .
private label Impact Testing
Resultado da Copy Link. cookiecrumble FedoraHat 1yr ago #192814 Edited 1yr ago. The video where you can see the torture and execution of a man, known as .
tibial torsion test of ankle joint by physiotutors|femoral anteversion and tibial torsion